原文:zhihu
c++手撕一个简化版的优先队列..
优先队列用于维护一组数据及其优先级,通常支持查找优先级最大(小)的队首元素,入队元素与弹出队首元素
在c#泛型优先队列中,优先值是显式的(PriorityQueue<TElement,TPriority>),也就是同时存储元素和优先值,且维护队首元素优先值最小
而在C++ STL中std::priority_queue<T>维护队首元素优先值最大,且优先值是隐式的,较小的元素有较小的优先值,默认的小于号比较器是std::less<>
也就是说std::priority_queue<int, vector<int>, std::greater<>> 维护最小值,std::priority_queue<int, vector<int>, std::less<>> 维护最大值
所以如果实际中优先值与元素类型没有关系,我们可以把存储类型更改为std::pair<TPriority, T>,或者新建类型绑定优先值与元素
我们可以利用最大二叉堆实现一个类似的优先队列
最大二叉堆是这样一颗完全二叉树(所有层,除了最后一层都一定是满的,且节点靠左排列)
且二叉堆中任意节点满足性质,节点大于所有其子节点
由于是完全二叉树,可以直接用数组存储树结构,令根节点位于下标0,则节点x的父节点为(x - 1) / 2 ,左右节点为2 * x + 1, 2 * x + 2
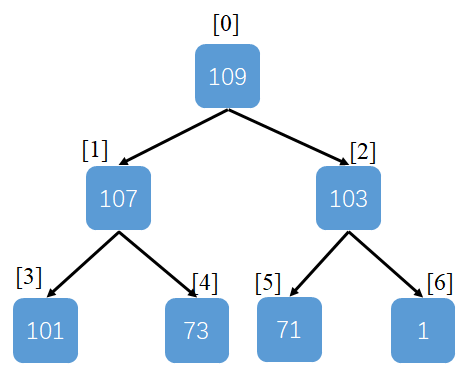
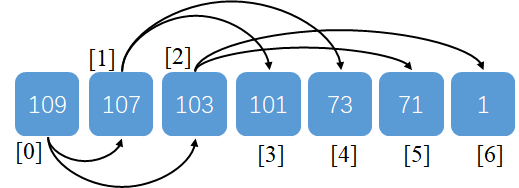
二叉堆的核心在于插入与删除,因为最大元素已经在数据开头了
先声明优先队列的主要成员
template<typename T, typename Compare = std::less<T>>
class PriorityQueue {
private:
using uz = std::size_t;
std::vector<T> _vec;
Compare _cmp;
public:
explicit PriorityQueue(Compare cmp = {}) : _vec{}, _cmp{cmp} {}
template<typename Iterator>
PriorityQueue(Iterator begin, Iterator end, Compare cmp = {}): _vec(begin, end),
_cmp{cmp} { _maintain_from_chaos(); }
inline auto size() { return _vec.size(); }
inline auto empty() { return _vec.empty(); }
inline auto clear() { _vec.clear(); }
T const &peek();
inline T const *try_peek();
template<typename ForwardAsT = T> void push(ForwardAsT &&value);
template<typename ...Args> void emplace(Args ...args);
T pop();
inline std::optional<T> try_pop();
private:
inline auto _father_of(uz x) {return (x - 1) >> 1;}
inline auto _left_of(uz x) {return (x << 1) | 1;}
void _maintain_up(uz current);
void _maintain_down(uz current);
inline void _maintain_from_chaos();
};
其中uz为std::size_t,_cmp是小于号(<),_vec是最大堆
因为队列可能为空,为查询最大元素与出队最大元素也提供了安全的try_peek(), try_pop
入队元素的函数为push与emplace
push会从实参拷贝(移动)构造新元素T,而
template<typename ...Args> void emplace(Args ...args);
的形参是T构造函数的参数,我们将在这个函数中利用std::vector::emplace_back原地构造对象,有些情况下可以节省一次拷贝或移动
这里
template<typename ForwardAsT = T> void push(ForwardAsT &&value);
的万能引用写成ForwardAsT &&而不是T&&的原因是在PriorityQueue<T, Compare>类内部,T已经被替换成具体的元素类型了,所以T&&是右值引用,而不是万能引用
比如
template<typename T> struct A {
void f(T&&) {
cout << "okay for overload of lvalue reference";
}
};
int main() {
int b = 2;
A<int>{}.f(b);
}
报错error: rvalue reference to type 'int' cannot bind to lvalue of type 'int', 而以下代码可以编译
template<typename T> struct A {
template<typename TT = T>
void f(TT&&) {
cout << "okay for overload of lvalue reference";
}
};
具体实现上,首先考虑入队,直接将新元素尾插二叉堆数组
template<typename ForwardAsT = T>
void push(ForwardAsT &&value) {
_vec.push_back(std::forward<ForwardAsT>(value));
_maintain_up(_vec.size() - 1);
}
而新插入的节点可能破坏了父节点的性质(比新节点还小),所以写一个_maintain_up(x)函数用于维护x的父节点的性质,如果父节点比x小,就不断地交换二者
void _maintain_up(uz current) {
while (current != 0) {
auto father = _father_of(current);
if (_cmp(_vec[father], _vec[current]))
std::swap(_vec[father], _vec[current]);
// if father < current , let current grow
else break;
current = father;
}
}
而出队时,首先交换二叉堆数组开头元素(根节点)与末尾元素,弹出并返回末尾的最大值
T pop() {
if (empty())
throw std::runtime_error("pop on a empty PriorityQueue");
std::swap(_vec.front(), _vec.back());
auto ret = std::move(_vec.back());
_vec.pop_back();
_maintain_down(0);
if (_vec.size() > 32 && _vec.size() * 2 < _vec.capacity())
_vec.shrink_to_fit();
return ret;
}
而此时根节点的性质可能被破坏,所以写一个_maintain_down(x)函数用于维护x节点的性质,如果x比最大的孩子小,就不断地交换二者
void _maintain_down(uz current) {
for (auto child = _left_of(current); child < _vec.size(); child = _left_of(current)) {
// while there is still any children for current node
if (auto sibling = child + 1; sibling < _vec.size() && _cmp(_vec[child], _vec[sibling]))
child = sibling;
// select biggest child
if (_cmp(_vec[current], _vec[child]))
std::swap(_vec[current], _vec[child]);
// if current < child, let child grow
else break;
current = child;
}
}
查询最大元素
T const &peek() {
if (empty())
throw std::runtime_error("peek on a empty PriorityQueue");
return _vec.front();
}
最后是构造函数,基本构造函数设计为迭代器形参
template<typename Iterator>
PriorityQueue(Iterator begin, Iterator end, Compare cmp = {}): _vec(begin, end),
_cmp{cmp} { _maintain_from_chaos(); }
由于初始二叉堆是无序的,在_maintain_from_chaos函数中从底向上遍历二叉堆的节点,都调用一遍_maintain_down维护自身性质即可
inline void _maintain_from_chaos() {
for (uz i = _vec.size(); i > 0;)
_maintain_down(--i);
}
再完善一下构造函数,支持std::initializer_list与可迭代类型
PriorityQueue(std::initializer_list<T> il, Compare cmp = {}) : PriorityQueue(il.begin(), il.end(), cmp) {}
template<typename Container> using UniIter = std::conditional_t<
std::is_rvalue_reference_v<Container>,
std::move_iterator<typename std::decay_t<Container>::iterator>,
typename std::decay_t<Container>::iterator>;
template<typename Container> explicit
PriorityQueue(Container &&container, Compare cmp = {}): PriorityQueue(
UniIter<decltype(container)>(container.begin()), UniIter<decltype(container)>(container.end()), cmp) {}
这样就完成啦
code: Github
使用例:pair的小根堆
int main() {
std::mt19937 rng{std::random_device{}()};
auto q1 = PriorityQueue<std::pair<int, int>, std::greater<>>{{114, 514}, {1919, 810}};
for (int i = 0; i < 17; i++)
q1.emplace(rng() % 4, rng() % 100);
while (!q1.empty()) {
auto [a, b] = q1.pop();
cout << "(" << a << ", " << b << "), ";
}
}
// (0, 57), (0, 89), (1, 4), (1, 29), (1, 40), (1, 42), (1, 50), (2, 3), (2, 23), (2, 57), (2, 65), (2, 75), (3, 0), (3, 26), (3, 85), (3, 86), (3, 87), (114, 514), (1919, 810),